Payment regulations in Europe: A comprehensive guide
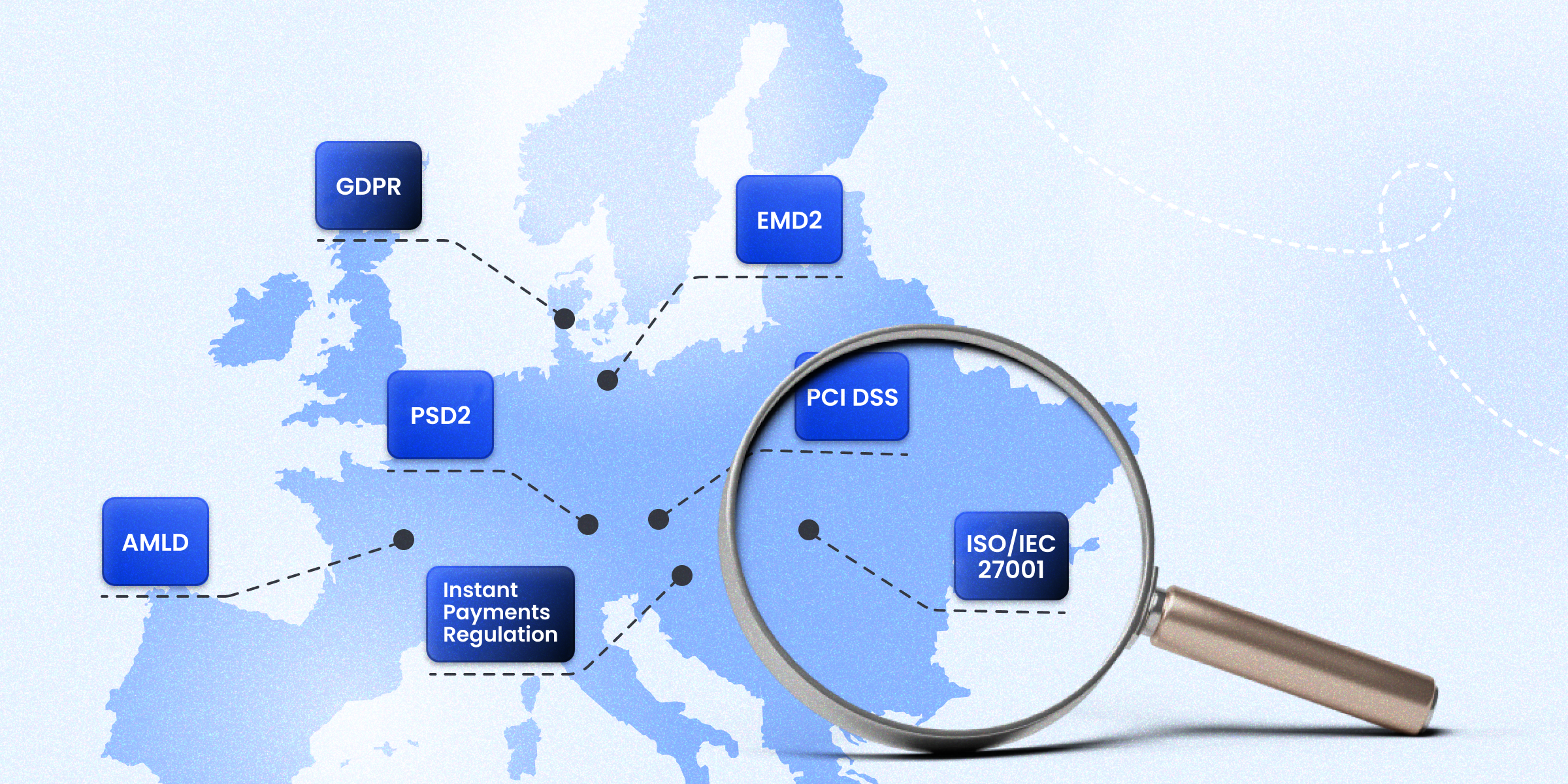
- Key payment regulations in Europe
- 1. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- 2. Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2)
- 3. Anti-Money Laundering Directives (AMLD)
- 4. Electronic Money Directive (EMD2)
- 5. Instant Payments Regulation
- Global standards influencing payment regulations in Europe
- 1. Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
- 2. ISO/IEC 27001
- Key regulatory bodies in Europe
Payment regulations in Europe are shaped by a combination of regional and global standards designed to ensure security, consumer protection, and financial stability. Understanding these regulations is crucial for businesses and individuals involved in financial transactions across the European Union (EU) and beyond.
This article provides an overview of key payment regulations in Europe, along with relevant global standards and the regulatory bodies that enforce them.
Key payment regulations in Europe
1. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)

The GDPR is one of the most comprehensive data protection laws in the world. It applies to any organisation that processes the personal data of individuals within the EU, regardless of where the organisation is based.
- Focus: The primary aim of GDPR is to protect individuals’ personal data and ensure their privacy rights.
- Scope: GDPR applies to data controllers and processors within the EU and those outside the EU if they offer goods or services to, or monitor the behaviour of, EU residents.
- Key requirements: Organisations must obtain explicit consent from individuals before processing their data, provide clear information on how data is used, allow individuals to access, correct, or delete their data, and notify authorities and affected individuals in case of a data breach. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties.
GDPR has set a high standard for data protection, influencing legislation worldwide and making personal data handling more transparent and accountable.
2. Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2)

PSD2 is a key regulatory framework that aims to enhance competition and innovation in the European payments market while improving consumer security.
- Focus: PSD2 covers various payment services, including online and mobile payments, credit transfers, and direct debits.
- Scope: It applies to payment service providers (PSPs) across the EU, including banks, fintech companies, and other financial institutions.
- Key requirements:
- Strong Customer Authentication (SCA): PSD2 requires multi-factor authentication to verify the identity of users in electronic payments, significantly enhancing transaction security.
- Open Banking: The directive mandates that banks give third-party providers access to customer account data with the customer’s consent. This drives competition and innovation and leads to the launch of new payment services and financial products.
PSD2 has revolutionised the payment industry in Europe by opening the market to new players and technologies while ensuring robust security measures.
3. Anti-Money Laundering Directives (AMLD)
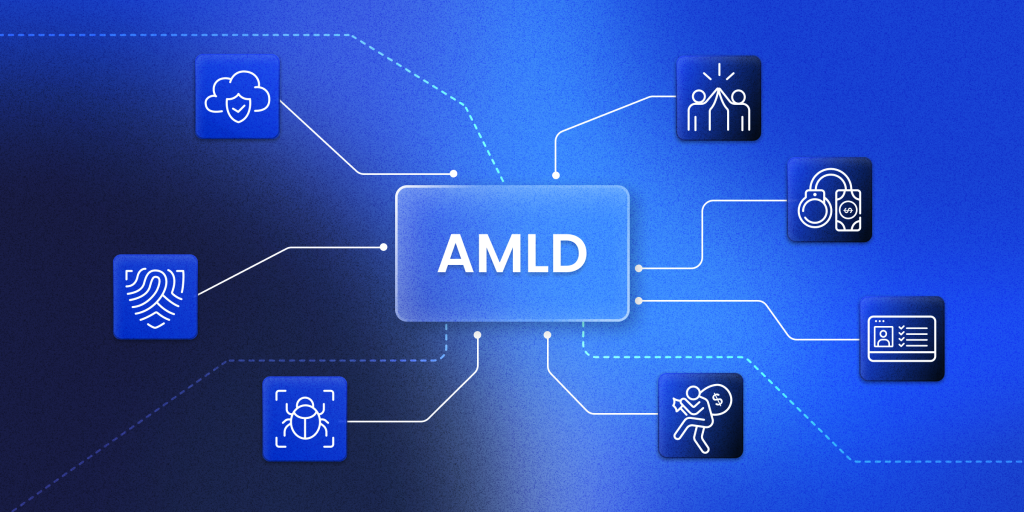
The AMLD establishes a comprehensive framework to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing within the EU.
- Focus: AMLD aims to protect the integrity of the financial system by preventing its use for illegal activities.
- Scope: The directives apply to various entities, including banks, financial institutions, legal professionals, and other businesses.
- Key requirements: These include customer due diligence (CDD) – a series of checks to verify clients’ identities, ongoing transaction monitoring, and reporting of suspicious activities to relevant authorities.
The latest directive, AMLD5, expands the scope to include virtual currencies, prepaid cards, and closer monitoring of high-risk third countries.
4. Electronic Money Directive (EMD2)

EMD2 regulates the issuance and management of electronic money (e-money) within the EU, ensuring consumer protection and financial stability.
- Focus: EMD2 governs how electronic money institutions (EMIs) operate, including issuing e-money and managing customer funds.
- Scope: The directive applies to all EMIs operating in the EU, including those offering digital wallets, prepaid cards, and other forms of e-money.
- Key requirements: EMIs must be licensed and meet specific prudential requirements, such as safeguarding customer funds, maintaining adequate capital, and ensuring transparency in fees and services.
EMD2 plays a crucial role in fostering trust and security in the digital payments landscape.
5. Instant Payments Regulation
Introduced in 2024, the Instant Payments Regulation aims to standardise and promote instant payment services across the EU.
- Focus: The regulation facilitates real-time payment processing, enhancing speed and convenience for consumers and businesses.
- Scope: It applies to all PSPs in the EU, ensuring that they offer instant payment options available 24/7, 365 days a year.
- Key requirements: PSPs must adhere to defined technical standards for instant payments, ensure high levels of security, and provide transparent pricing. Additionally, consumers must be informed about the availability and terms of instant payment services.
The Instant Payments Regulation is designed to encourage the adoption of faster payment methods, supporting the EU’s broader goals of digital transformation and financial inclusion.
Global standards influencing payment regulations in Europe
1. Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)

PCI DSS is a global standard that sets security requirements for organisations handling credit card data.
- Focus: The standard aims to protect cardholder data from breaches and fraud.
- Scope: PCI DSS applies to all entities that store, process, or transmit cardholder data, including merchants, payment processors, and financial institutions.
- Key requirements: The standard includes requirements for securing cardholder data, such as encryption, maintaining a secure network, implementing strong access control measures, as well as regularly monitoring and network testing.
Compliance with PCI DSS is critical for preventing data breaches and maintaining consumer trust.
2. ISO/IEC 27001

ISO/IEC 27001 is an international standard for information security management systems (ISMS).
- Focus: The standard provides a framework for managing sensitive company information to ensure it remains secure.
- Scope: It applies to all organisations that manage information systems, regardless of size or industry.
- Key requirements: ISO/IEC 27001 includes risk assessment and management processes, information security policies, and procedures, as well as continuous monitoring and improvement of security practices.
Adherence to ISO/IEC 27001 helps organisations protect their data assets and comply with various legal and regulatory requirements.
Key regulatory bodies in Europe
There are several regulatory bodies responsible for enforcing payment regulations in Europe and ensuring compliance:
- European Banking Authority (EBA): The EBA provides regulatory and supervisory guidelines to ensure the consistency and quality of regulation and supervision across the EU banking sector. It plays a vital role in implementing PSD2 and other financial regulations.
- European Central Bank (ECB): The ECB oversees the stability and efficiency of the Eurozone’s financial system. It is involved in the supervision of payment systems and contributes to the formulation of monetary policy.
- National Competent Authorities (NCAs): Each EU member state has its regulatory authorities, such as the Autorité de Contrôle Prudentiel et de Résolution (ACPR) in France. These bodies enforce EU directives and local regulations, ensuring compliance at the national level.
Conclusion
Merchants should be vigilant about choosing a PSP that prioritises compliance and security. It’s essential to partner with a PSP that adheres to the above-mentioned regulations and implements robust data protection measures. This ensures the safety of customer information and mitigates the risk of legal issues.
At Payop, we understand that navigating the intricate landscape of payment regulations in Europe is crucial for providing secure and reliable financial services. Compliance with these regulations not only ensures we meet legal requirements but also helps us build and maintain trust with our customers.