What is an EFT payment?
Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) is a digital money movement from one bank account to another. This process is typically done through computer systems that don’t require direct involvement of bank staff.
Here’s a complete guide to the various types of EFTs and how you can use them to optimise your payment processes.
Types of EFT payments
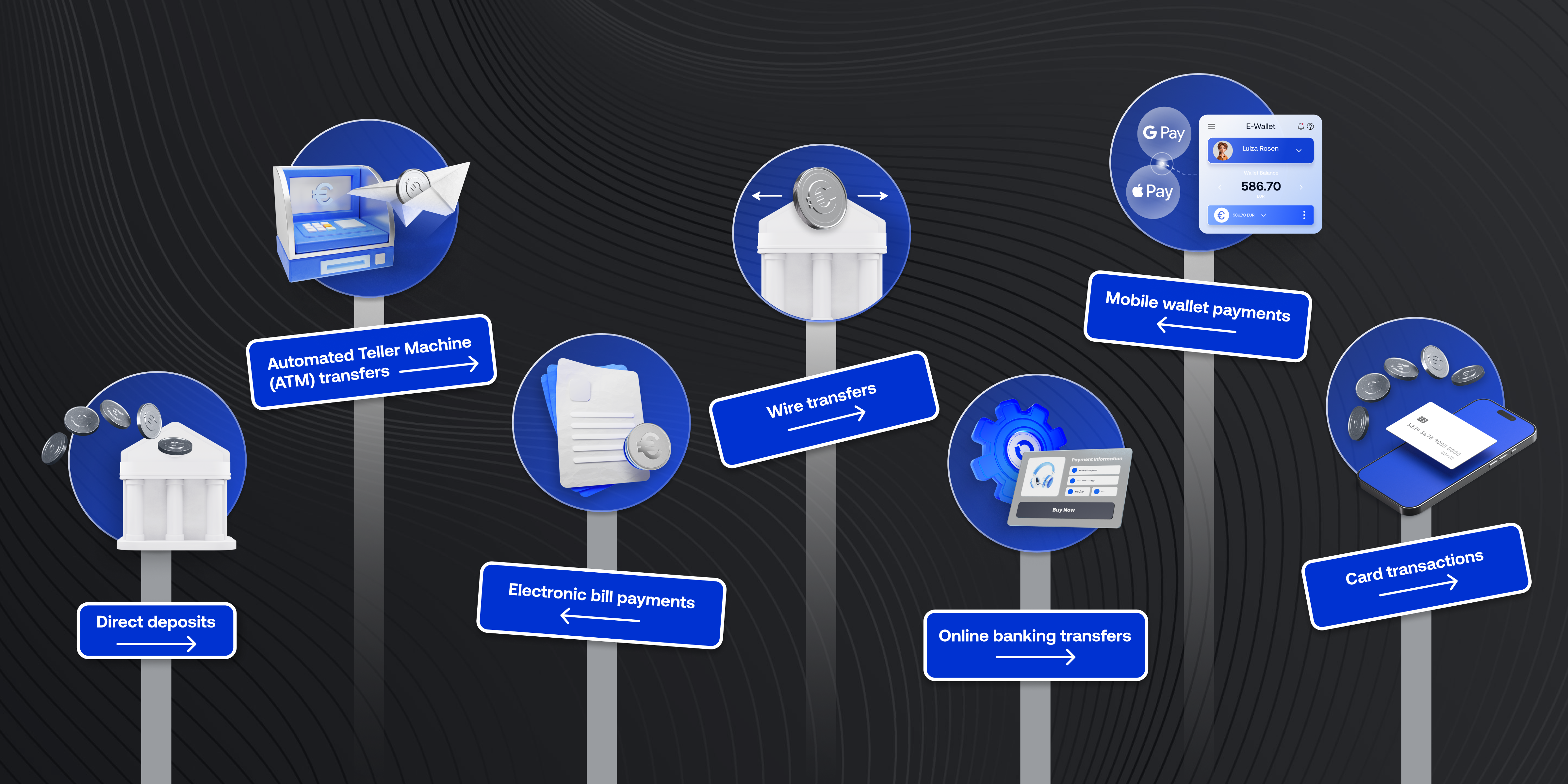
EFT payments cover a range of transactions in which money is transferred electronically. Unlike traditional methods such as cash or cheques, EFTs use digital channels to transfer funds, making the process more efficient and convenient.
Common types of EFT payments include:
- Direct deposits: Employers use EFT to deposit salaries directly into employees’ bank accounts.
- Automated Teller Machine (ATM) transfers: Money transfers between accounts through ATMs.
- Electronic bill payments: Utility bills, credit card bills, and other recurring payments made electronically.
- Wire transfers: Fund transfers between different banks or financial institutions, often used for large or urgent transactions.
- Online banking transfers: Customers move money between accounts or to others through online banking platforms.
- Card transactions: Purchases made using a debit card are also a form of EFT, where money is directly transferred from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account.
- Mobile wallet payments: Transactions made through mobile wallets (like Apple Pay, Google Pay, or other digital wallets) where funds are transferred electronically from the user’s bank account or linked card to the merchant or recipient.
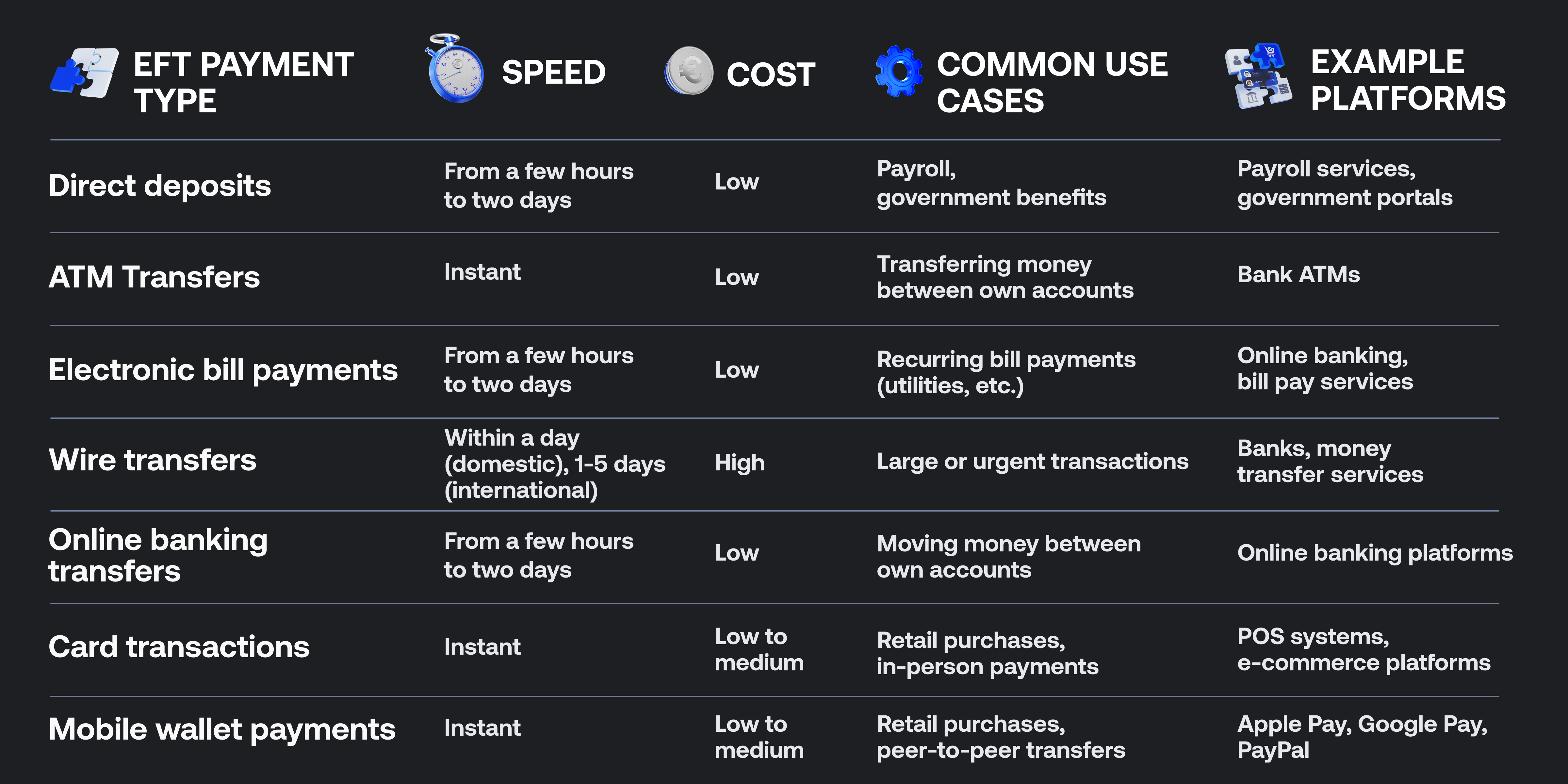
Comparison of different types of EFT payments
How EFT payments work
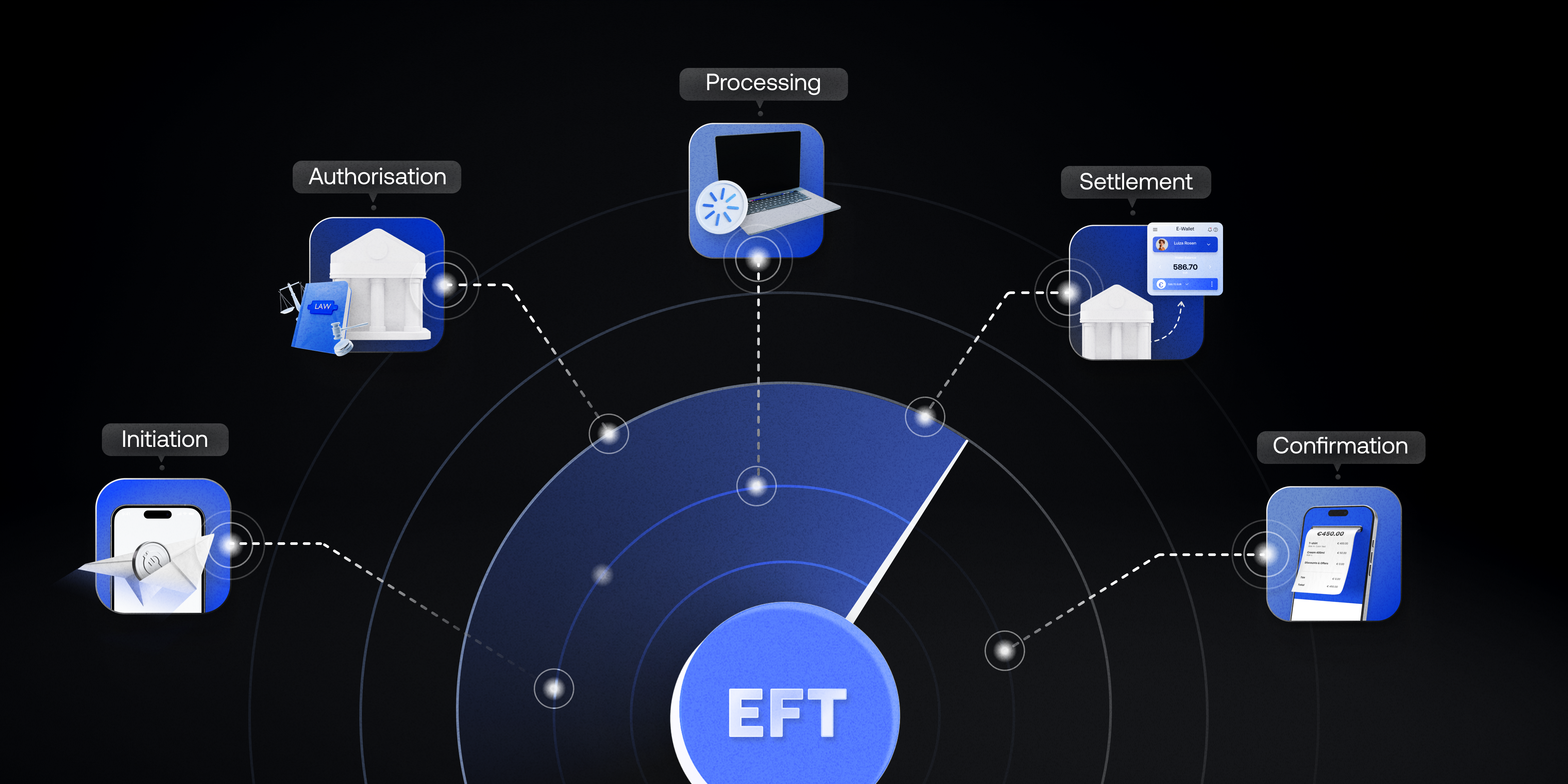
EFT payments are processed through a computer network that enables easy funds transfer between financial institutions. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how it works:
- Initiation: The payer initiates the payment through an online banking app, ATM, or point-of-sale system.
- Authorisation: The payment request is sent to the payer’s bank for authorisation. The bank checks if sufficient funds are available and the transaction is legitimate.
- Processing: Once authorised, the bank debits the payer’s account and sends the payment instructions to the recipient’s bank.
- Settlement: The recipient’s bank credits the funds to the recipient’s account, completing the transaction.
- Confirmation: Both the payer and the recipient are notified of the successful transaction.
Common use cases of EFT payments

EFT payments are widely used in various scenarios:
- Payroll: Companies use EFT to pay employees directly into their bank accounts, streamlining payroll processes.
- Bill payments: Consumers and businesses use EFT to automate recurring payments, ensuring on-time payments without manual intervention.
- E-commerce: Online shopping platforms use EFT for payments between customers and merchants, often through debit or credit card transactions.
- Peer-to-peer transfers: You can quickly send money to friends or family through mobile banking apps or digital wallets.
Benefits of EFT payments compared to traditional methods

EFT payments offer numerous advantages, making them a preferred method of payment:
- Faster payment processing: EFT payments allow merchants to receive funds quicker than traditional payment methods like checks. Transactions are processed often within the same day. It ensures a steady cash flow and better operations management.
- Reduced transaction costs: EFT payments have lower fees than older traditional methods. This cost-efficiency is particularly beneficial for merchants handling high transaction volumes.
- Improved security: EFT payments are highly secure, utilising encryption and multi-factor authentication to protect against fraud. For merchants, this means reduced risk of chargebacks and fraudulent transactions, leading to fewer disputes and losses.
- Automation: EFT payments can be automated, making it easier for merchants to manage recurring billing, payroll, and supplier payments. This reduces administrative costs, freeing time and resources to focus on business development.
Payment diversity with Payop
Payop provides merchants with a wide choice of payment methods, ensuring you can cater to diverse customer preferences. With over 500 international and local payment methods and over 100 currencies, you can expand your business reach, enhance customer satisfaction, and optimise your payment processing, all while maintaining security and efficiency.
Contact our team at sales@payop.com to learn more.